The basic process of powder metallurgy includes the following steps:
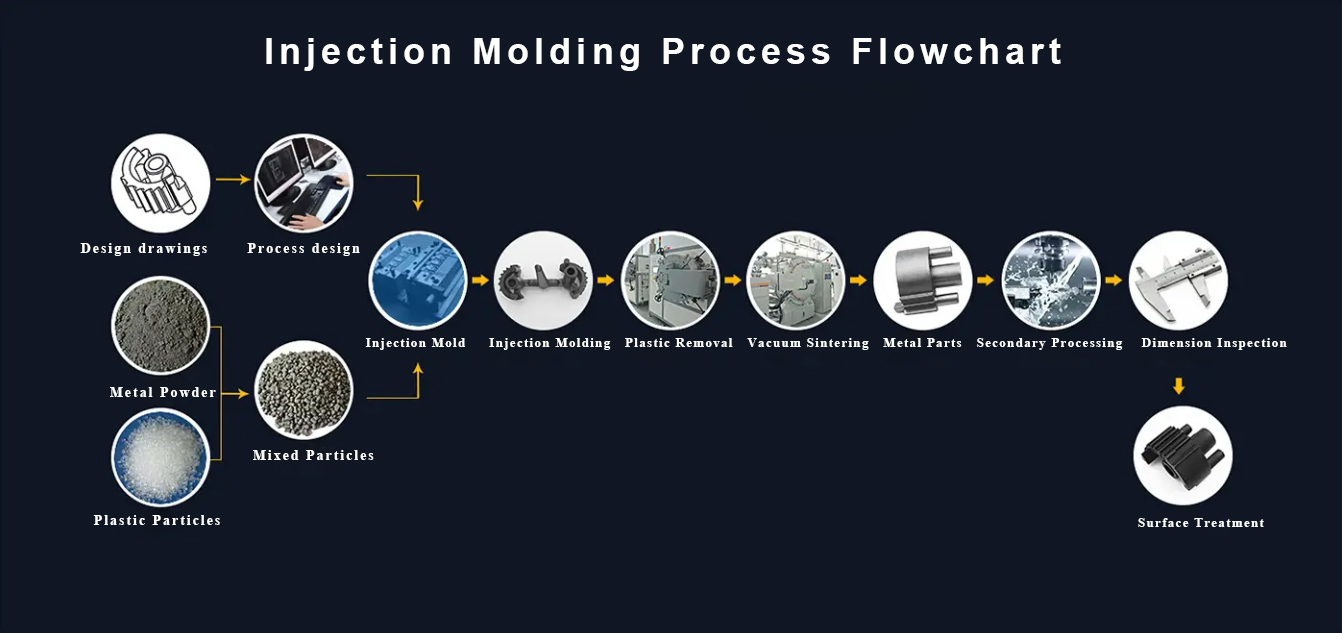
1. Preparation of raw materials in powder form. There are generally two types of powder preparation methods: mechanical and physical-chemical methods. Mechanical methods include mechanical crushing and atomization, while physical-chemical methods include electrolytic corrosion, reduction, synthesis, reduction-synthesis, gas-phase deposition, liquid-phase deposition, and electrolysis, among which reduction, atomization, and electrolysis are widely used.
2. Formation of shaped blocks from the powder. The purpose of forming is to produce pressed blocks with specific shapes and sizes, and to give them a certain density and strength. Forming methods are mainly divided into pressure forming and non-pressure forming, among which the most commonly used method is mold forming.
3. Sintering of the blocks. Sintering is a critical process in the powder metallurgy process. After forming, the pressed blocks are sintered to achieve the desired final physical and mechanical properties. Sintering can be divided into solid-phase sintering of single-element systems and multi-element systems. For solid-phase sintering, the sintering temperature is lower than the melting point of the metal and alloy used, while for liquid-phase sintering of multi-element systems, the sintering temperature is generally lower than the melting point of the harder component, but higher than the melting point of the easier component. In addition to conventional sintering, there are also special sintering processes such as loose packing sintering, melt infiltration, and hot pressing.
4. Post-treatment of the products. After sintering, various post-treatment processes can be used according to the different requirements of the final product, such as finishing, oil immersion, machining, heat treatment, and electroplating. In recent years, some new processes such as rolling and forging have also been applied to the processing of sintered powder metallurgy materials, achieving ideal results.











